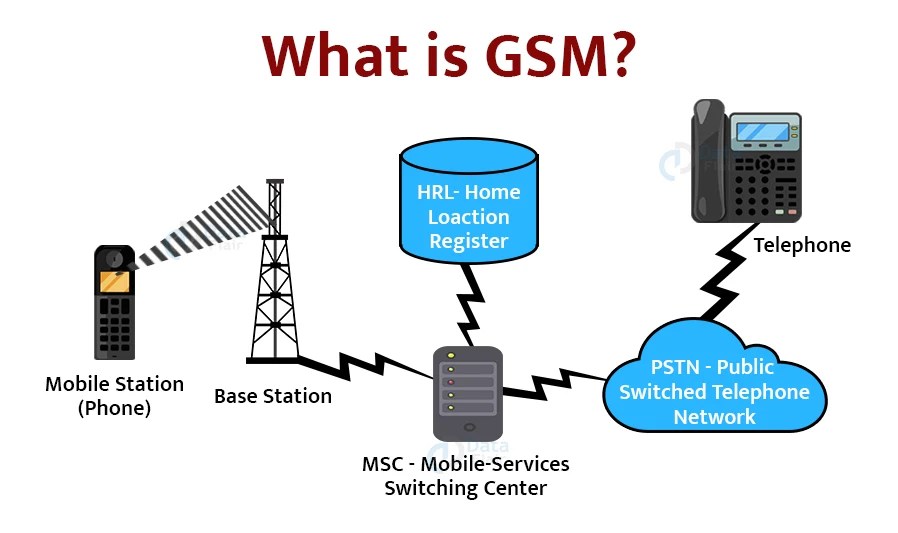
What is GSM Network?
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is a standardized digital cellular network used for mobile telephony. It is the most widely used mobile network standard in the world, with over 5 billion subscribers. GSM networks operate in the 900 MHz and 1800 MHz frequency bands.
GSM networks are used for a variety of purposes, including voice calls, text messaging, and data services. GSM networks are also used for a variety of applications, such as mobile banking, mobile payments, and mobile commerce.
GSM networks have a number of advantages over other mobile network standards. GSM networks are more reliable and secure than other mobile network standards. GSM networks are also more efficient than other mobile network standards, which means that they can handle more traffic with less bandwidth.
GSM networks have played a major role in the development of mobile communications. GSM networks have made it possible for people to stay connected with each other, regardless of where they are in the world.
GSM Network Meaning
GSM (Global System for Mobile Communications) is a standardized digital cellular network used for mobile telephony. It is the most widely used mobile network standard in the world, with over 5 billion subscribers. GSM networks operate in the 900 MHz and 1800 MHz frequency bands.
- Global: GSM networks are used in over 220 countries and territories.
- Digital: GSM networks use digital technology to transmit voice and data.
- Cellular: GSM networks are divided into small geographic areas called cells.
- Mobile: GSM networks are designed for use by mobile devices, such as cell phones and smartphones.
- Communications: GSM networks are used for a variety of communication purposes, including voice calls, text messaging, and data services.
- Secure: GSM networks are secure, thanks to the use of encryption and authentication technologies.
- Reliable: GSM networks are reliable, even in areas with poor signal strength.
GSM networks have played a major role in the development of mobile communications. GSM networks have made it possible for people to stay connected with each other, regardless of where they are in the world.
Global
The global reach of GSM networks is one of its key advantages. GSM networks are used in over 220 countries and territories, which means that users can stay connected wherever they are in the world. This is especially important for business travelers and people who frequently travel internationally.
- Ubiquity: GSM networks are widely available, even in remote areas. This means that users can stay connected even when they are traveling off the beaten path.
- Roaming: GSM networks allow users to roam between different countries and networks without having to change their SIM card. This makes it easy to stay connected while traveling abroad.
- Interoperability: GSM networks are interoperable, which means that users can use their devices on any GSM network in the world. This makes it easy to stay connected with friends and family who live in different countries.
The global reach of GSM networks is a major factor in its success. GSM networks have made it possible for people to stay connected with each other, regardless of where they are in the world.
Digital
The digital nature of GSM networks is one of its key advantages. GSM networks use digital technology to transmit voice and data, which offers a number of advantages over analog networks.
- Clarity: Digital signals are less susceptible to interference than analog signals, which results in clearer voice calls and data transmissions.
- Security: Digital signals are more difficult to intercept and eavesdrop on than analog signals, which makes GSM networks more secure.
- Efficiency: Digital signals can be compressed more efficiently than analog signals, which allows GSM networks to transmit more data in a given amount of bandwidth.
- Capacity: Digital networks can handle more users and traffic than analog networks, which makes them ideal for use in densely populated areas.
The digital nature of GSM networks has made them the most popular mobile network standard in the world. GSM networks offer a number of advantages over analog networks, including clarity, security, efficiency, and capacity.
Cellular
The cellular nature of GSM networks is one of its key advantages. GSM networks are divided into small geographic areas called cells, which allows them to provide a number of benefits.
- Coverage: Cellular networks can provide coverage in areas where it would be impractical or impossible to provide wired coverage. This is especially important in rural areas and remote locations.
- Capacity: Cellular networks can handle a large number of users and traffic, which makes them ideal for use in densely populated areas.
- Mobility: Cellular networks allow users to move around freely while staying connected. This is essential for mobile devices, such as cell phones and smartphones.
- Efficiency: Cellular networks are efficient in terms of spectrum usage. This means that they can provide a high level of coverage and capacity without using a lot of spectrum.
The cellular nature of GSM networks has made them the most popular mobile network standard in the world. GSM networks offer a number of advantages over other mobile network standards, including coverage, capacity, mobility, and efficiency.
Mobile
The mobile nature of GSM networks is one of its key advantages. GSM networks are designed for use by mobile devices, such as cell phones and smartphones, which allows users to stay connected while on the move. This is essential for people who need to stay connected for business, personal, or safety reasons.
- Convenience: Mobile networks allow users to make and receive calls, send and receive text messages, and access data services from anywhere within the network's coverage area. This is especially important for people who are always on the go.
- Productivity: Mobile networks allow users to stay connected with colleagues, customers, and partners while they are away from the office. This can help to improve productivity and efficiency.
- Safety: Mobile networks can be used to call for help in case of an emergency. This can be especially important for people who work in remote or dangerous areas.
The mobile nature of GSM networks has made them the most popular mobile network standard in the world. GSM networks offer a number of advantages over other mobile network standards, including convenience, productivity, and safety.
Communications
GSM networks are used for a wide range of communication purposes, including voice calls, text messaging, and data services. This versatility is one of the key reasons for GSM's popularity and success.
- Voice calls: GSM networks are used for voice calls, which is one of the most basic and essential forms of communication. GSM voice calls are clear and reliable, even in areas with poor signal strength.
- Text messaging: GSM networks are also used for text messaging, which is a quick and easy way to send and receive short messages. Text messaging is a popular way to stay in touch with friends and family, and it is also used for business purposes.
- Data services: GSM networks are also used for data services, which allow users to access the internet and other online services. Data services are essential for a variety of purposes, including browsing the web, checking email, and downloading apps.
The versatility of GSM networks makes them a valuable tool for communication. GSM networks can be used for a variety of purposes, from staying in touch with friends and family to conducting business.
Secure
The security of GSM networks is one of its key advantages. GSM networks are secure thanks to the use of encryption and authentication technologies, which protect user data from eavesdropping and unauthorized access.
- Encryption: GSM networks use encryption to protect user data from eavesdropping. Encryption scrambles data so that it cannot be read by unauthorized parties.
- Authentication: GSM networks use authentication technologies to verify the identity of users. Authentication ensures that only authorized users can access the network and user data.
The security of GSM networks is essential for protecting user privacy and data. GSM networks are used for a variety of purposes, including banking, mobile payments, and mobile commerce. The security of GSM networks helps to protect users from fraud and identity theft.
Reliable
The reliability of GSM networks is one of its key advantages. GSM networks are reliable even in areas with poor signal strength, which makes them ideal for use in remote and rural areas.
- Coverage: GSM networks have a wide coverage area, which means that users can stay connected even in remote areas. This is especially important for people who live or work in rural areas.
- Robustness: GSM networks are robust and can withstand interference and signal fluctuations. This means that users can stay connected even in areas with poor signal strength.
- Handoffs: GSM networks use a system of handoffs to seamlessly transfer calls between different cells. This ensures that users can stay connected even when they are moving around.
- Battery life: GSM networks are designed to be power efficient, which means that users can get longer battery life from their devices.
The reliability of GSM networks is essential for providing users with a consistent and reliable mobile experience. GSM networks are used for a variety of purposes, including voice calls, text messaging, and data services. The reliability of GSM networks ensures that users can stay connected even in areas with poor signal strength.
GSM Network Meaning FAQs
This section provides answers to frequently asked questions about GSM network meaning. These questions aim to clarify common misconceptions and provide a deeper understanding of the topic.
Question 1: What does GSM stand for?
Answer: GSM stands for Global System for Mobile Communications.
Question 2: What is the difference between GSM and other mobile network standards?
Answer: GSM is a digital cellular network standard that uses a narrowband frequency range. It is known for its global reach, security, and reliability. Other mobile network standards include CDMA, TDMA, and LTE, which differ in terms of technology, frequency bands, and capabilities.
Question 3: What are the advantages of using GSM networks?
Answer: GSM networks offer several advantages, including:
Global coverage: GSM networks are widely available in over 220 countries and territories.Reliability: GSM networks are known for their stability and resilience, even in areas with poor signal strength.Security: GSM networks employ robust encryption and authentication technologies to protect user data and communications.Interoperability: GSM networks allow seamless roaming between different network operators and countries.Question 4: What are the limitations of GSM networks?
Answer: While GSM networks offer many advantages, they also have some limitations, such as:
Speed: GSM networks have a lower data transfer rate compared to newer technologies like 4G and 5G.Capacity: GSM networks have a limited capacity, which can lead to congestion during peak usage times.Question 5: Is GSM still relevant in today's mobile landscape?
Answer: Yes, GSM networks continue to play a significant role in the mobile landscape, particularly in developing countries and rural areas. While newer technologies offer faster speeds and greater capacity, GSM remains widely adopted due to its affordability, reliability, and global coverage. It is especially important for basic voice calls and SMS messaging.
Question 6: What is the future of GSM networks?
Answer: GSM networks are expected to continue to coexist with newer technologies for the foreseeable future. While they may gradually decline in developed markets, they will likely remain essential in regions with limited infrastructure and low bandwidth requirements. Additionally, GSM technology is being explored for new applications, such as IoT and M2M communication.
Summary of key takeaways or final thought: GSM networks have revolutionized mobile communications, providing a reliable and secure platform for voice calls, text messaging, and data services. While newer technologies offer enhanced capabilities, GSM remains a vital technology in the global mobile landscape, especially for basic connectivity and in areas with limited infrastructure.
Transition to the next article section: This concludes our exploration of GSM network meaning and its key aspects. In the next section, we will delve into the historical development and evolution of GSM technology.
GSM Network Meaning
This exploration of GSM network meaning has highlighted the significance and widespread adoption of GSM technology in the global mobile landscape. GSM networks have revolutionized mobile communications, providing a reliable and secure platform for voice calls, text messaging, and data services. Their global reach, affordability, and interoperability have made them accessible to billions of users worldwide.
While newer technologies offer enhanced capabilities, GSM remains a vital technology, particularly in developing countries and rural areas with limited infrastructure. It continues to play a crucial role in providing basic connectivity and enabling essential services. Additionally, GSM technology is being explored for new applications, such as IoT and M2M communication.
In conclusion, GSM networks have had a transformative impact on mobile communications and continue to play a fundamental role in connecting people around the world. Their legacy of reliability, security, and global reach will ensure their continued relevance in the years to come.
Determine The Age Of Aunjanue Ellis.
10 Suave White Haired Guys That Will Make You Swoon
Funny Times With Katt Williams' Children: Bringing Out The Laughter.